
Key Highlights of the Foreign Trade Policy, 2023
Summary
The Foreign Trade Policy 2023 is a comprehensive policy framework announced by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade, Department of Commerce, Government of India. Its key objective is to promote India’s exports and enhance its competitiveness in the global market. The policy is designed to be dynamic and responsive to the emerging trade scenario, with a focus on promoting exports from the grassroots and streamlining processes for e-commerce exports.
The policy sets sector-specific targets to achieve the goal of one trillion-dollar merchandise exports and one trillion-dollar services exports by 2030. It also aims to make Indian Rupees a global currency and facilitate international trade settlement in INR. The policy emphasizes greater engagement with states and districts to promote exports and develop them as export hubs.
The policy also includes a consultative mechanism to resolve issues of trade and industry, and a restructuring of the Department of Commerce to make it future-ready. The policy approach has shifted from incentives to tax remission, with a focus on greater trade facilitation through technology, automation, and continuous process re-engineering.
Overall, the Foreign Trade Policy 2023 aims to provide policy continuity and a responsive framework to promote India’s exports and enhance its competitiveness in the global market.
Key Approach
The Key Approach to the policy is based on four (4) pillars:
(i) From Incentives to Tax Remission;
(ii) Export promotion through collaboration – Exporters, States, Districts, Indian Missions;
(iii) Ease of doing business, reduction in transaction cost and e-initiatives; and
(iv) Focus on Emerging Areas – E-Commerce Developing Districts as Export Hubs and streamlining SCOMET policy.
Key Highlights
1. Ease of Doing Business, Reduction in Transaction Cost and e-Initiatives:
1.1 Online approvals without Physical Interface
- Automatic approval of various permissions under Foreign Trade Policy based on process simplification and technology implementation.
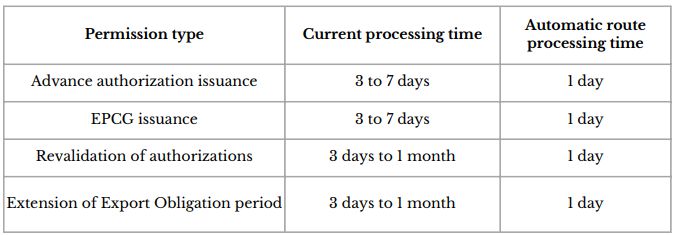
- Reduction in processing time and immediate approval of applications under automatic route for exporters:
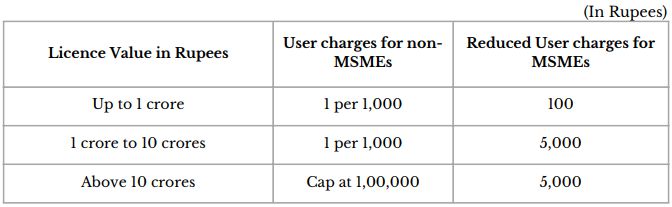
1.2 Reduction in user charges for MSMEs under AA and EPCG
- Application fee being reduced for Advance Authorization and EPCG Schemes
- Will benefit 55-60% of exporters who are MSMEs
- Fee structure as shown below:
1.3 E-Certificate of Origin
- Revamp of the e-Certificate of Origin platform proposed- to provide for self- certification of CoOs as well as automatic approval of CoOs, where feasible
- Initiatives for electronic exchange of CoO data with partner countries envisaged.
1.4 Paperless filing of Export Obligation Discharge Applications
- All authorisation redemption applications to be paperless – This is in addition to application process for issuance being already paperless. With this, the entire lifecycle of the authorization shall become paperless
2. Export Promotion Initiatives
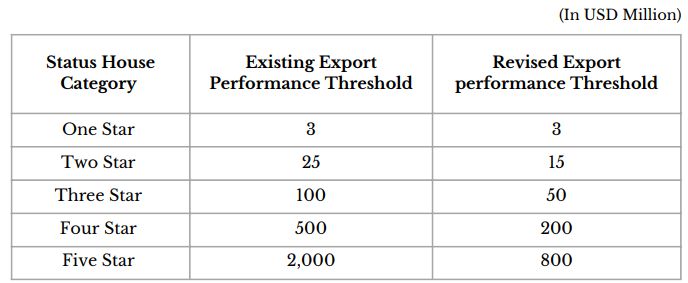
2.1 Status Holder Export Thresholds Rationalised
Export performance threshold for Recognition of Exporters as Status Holders rationalized. Enabling more exporters to achieve higher status and reduced transaction cost for exports.
2.2 Merchanting Trade Reform
To boost merchanting activities from India – Merchanting trade involving shipment of goods from one foreign country to another foreign country without touching Indian ports, involving an Indian intermediary is allowed subject to compliance with RBI guidelines, except for goods/items in the CITES and SCOMET list
2.3 Rupee Payment to be accepted under FTP Schemes
- Effective step towards internationalisation of Rupee
- FTP benefits extended for rupee realisations through special Vostro accounts setup as per RBI circular issued on 11 July 2022
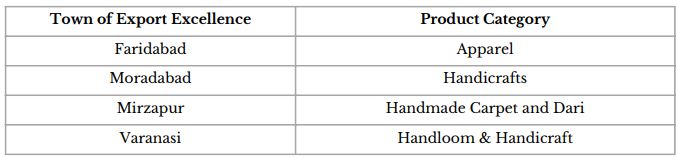
2.4 Towns of Export Excellence
- Four new towns of export excellence declared:
- These 4 new towns of export excellence (TEE) are in addition to the already existing 39 towns of export excellence
- This scheme gives thrust to cluster based economic development
- TEEs are industrial clusters that are recognized based on their export performance
- Recognition to these industrial clusters is granted with a view to maximize their potential and enable them to move up the value chain and to tap new markets
- Benefits under TEE Scheme are:
Recognition –
- Helps in getting recognition/credibility attached to industrial units of the region/town while exploring/expanding into newer markets
- Puts such industrial units/town on the global stage.
MAI Scheme –
- Recognized associations of units are provided financial assistance under Market Access Initiative Scheme on priority basis, for export promotion projects for marketing, capacity building and technological services.
- Through this scheme such units can get financial assistance to visit various trade exhibitions/fairs for exploring more marketing avenues.
Common Service Provider Facility –
- Common Service Providers in TEE are entitled for Authorisation under EPCG Scheme which can help in increasing the competitiveness of the cluster and provide enabling environment
- This arrangement gives facility to exporters to not own all the infrastructure for conversion from inputs to final export products
3. Districts as Export Hubs Initiative
3.1 States and Districts as Partners in Export Promotion
- Districts as Export Hubs aims to boost India’s foreign trade by decentralizing export promotion
- Bring a greater level of awareness and commitment regarding exports at the district level
- Identification of products/services in all the districts
- Create institutional mechanisms at the State and District level to strategize exports (State Export Promotion Committee & District Export Promotion Committee)
- Preparation of District Export Action Plans (DEAPs) outlining the action plan to promote identified products and services
- Make States and Districts meaningful stakeholders and active participants
3.2 Capacity Building at District level
- Capacity building to create new exporters and identification of new markets
- Training, handholding, and outreach programs by DGFT field offices in coordination with District Industries Centers
- Regional Authorities of DGFT working with the States/UTs to prepare District specific Export Plans
- Export promotion outreach programs in districts to focus on branding, packaging, design and marketing of identified product & services
3.3 Infrastructure and Logistics Development Intervention
- To address Infrastructure and Logistics bottlenecks impeding exports
- Districts to focus on development of logistics, testing facilities, connectivity for exports and other export-oriented ecosystem
- Convergence of ongoing schemes to support these initiatives
4. E-Commerce Exports
4.1 Facilitation for E-Commerce Exports
- All FTP benefits to be extended to e-Commerce exports
- Necessary enablement of IT systems in Department of Commerce, Post, CBIC to be undertaken in the six months
- To streamline e-Commerce export facilitation – Guidelines being formulated in consultation with other ministries to facilitate further exports under e-Commerce
- Special outreach and training activities for small e-commerce exporters
- Handholding through industry and knowledge partners
- Value limit for exports through courier is increased to Rs.10,00,000 per consignment
4.2 Dak Niryat Facilitation
Dak Ghar Niryat Kendras shall be operationalised throughout the country to work in a hub-and-spoke model with Foreign Post Offices (FPOs) to facilitate cross-border e-Commerce and to enable artisans, weavers, craftsmen, MSMEs in the hinterland and land-locked regions to reach international markets
4.3 E-Commerce Export Hubs
- Designated hubs with warehousing facility to be notified, to help e-commerce aggregators for easy stocking, customs clearance and returns processing
- Processing facility to be allowed for last mile activities such as labelling, testing, repackaging etc
5. Steps to Boost Manufacturing
- Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Parks (PM MITRA) scheme has been added as an additional scheme eligible to claim benefits under CSP(Common Service Provider) Scheme of Export Promotion capital Goods Scheme(EPCG)
- Dairy sector to be exempted from maintaining Average Export Obligation – to support dairy sector to upgrade the technology
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) of all types, Vertical Farming equipment, Wastewater Treatment and Recycling, Rainwater harvesting system and Rainwater Filters, and Green Hydrogen are added to Green Technology products – will now be eligible for reduced Export Obligation requirement under EPCG Scheme
- Special Advance Authorisation Scheme extended to export of Apparel and Clothing sector under para 4.07 of HBP on self-declaration basis to facilitate prompt execution of export orders – Norms would be fixed within fixed time-frame
- Benefits of Self-Ratification Scheme for fixation of Input-Output Norms extended to 2 star and above status holders in addition to Authorised Economic Operators at present
- Fruits and Vegetables exporters are being included for double weightage for counting export performance under eligibility criteria for Status House certification. This is in addition to existing MSME sector who also get double weightage
6. Special One-time Amnesty Scheme for Default in Export Obligations
- Government is strongly committed to reducing litigation and fostering trustbased relationships to help alleviate issues faced by exporters
- In line with the “Vivaad se Vishwaas” initiative, which sought to settle tax disputes amicably, Government is introducing a special one-time Amnesty Scheme to address non-compliance in Export Obligations by Advance Authorization and EPCG authorization holders
- All pending cases of default in Export Obligation (EO) of authorizations mentioned can be regularized by the authorization holder on payment of all customs duties exempted in proportion to unfulfilled Export Obligation and maximum interest is capped at 100% of such duties exempted. No interest is payable on the portion of Additional Customs Duty and Special Additional Customs Duty
- Amnesty scheme shall be available for a limited period, up to 30.09.2023
- Cases under investigation for fraud and diversion are not eligible for this scheme
7. Emphasis on Streamlining SCOMET Licensing Procedure
- Focus of FTP 2023 on Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET)
- Policy for export of dual use items under SCOMET consolidated at one place for ease of understanding and compliance by industry
- SCOMET policy emphasizes India’s export control in line with its International commitments under various export control regimes (Wassenaar arrangement, Australia group and Missile Technology Control Regime) to control trade in sensitive and dual use items including software and technology
- Recent policy changes introduced such as general authorizations for export of certain SCOMET items to streamline licensing of these items to make export of SCOMET items globally competitive.
- Focus on simplifying policies to facilitate export of dual-use high-end goods/technology such as UAV/Drones, Cryogenic Tanks, Certain chemicals etc
